Photo by James St. John licensed under CC BY 2.0
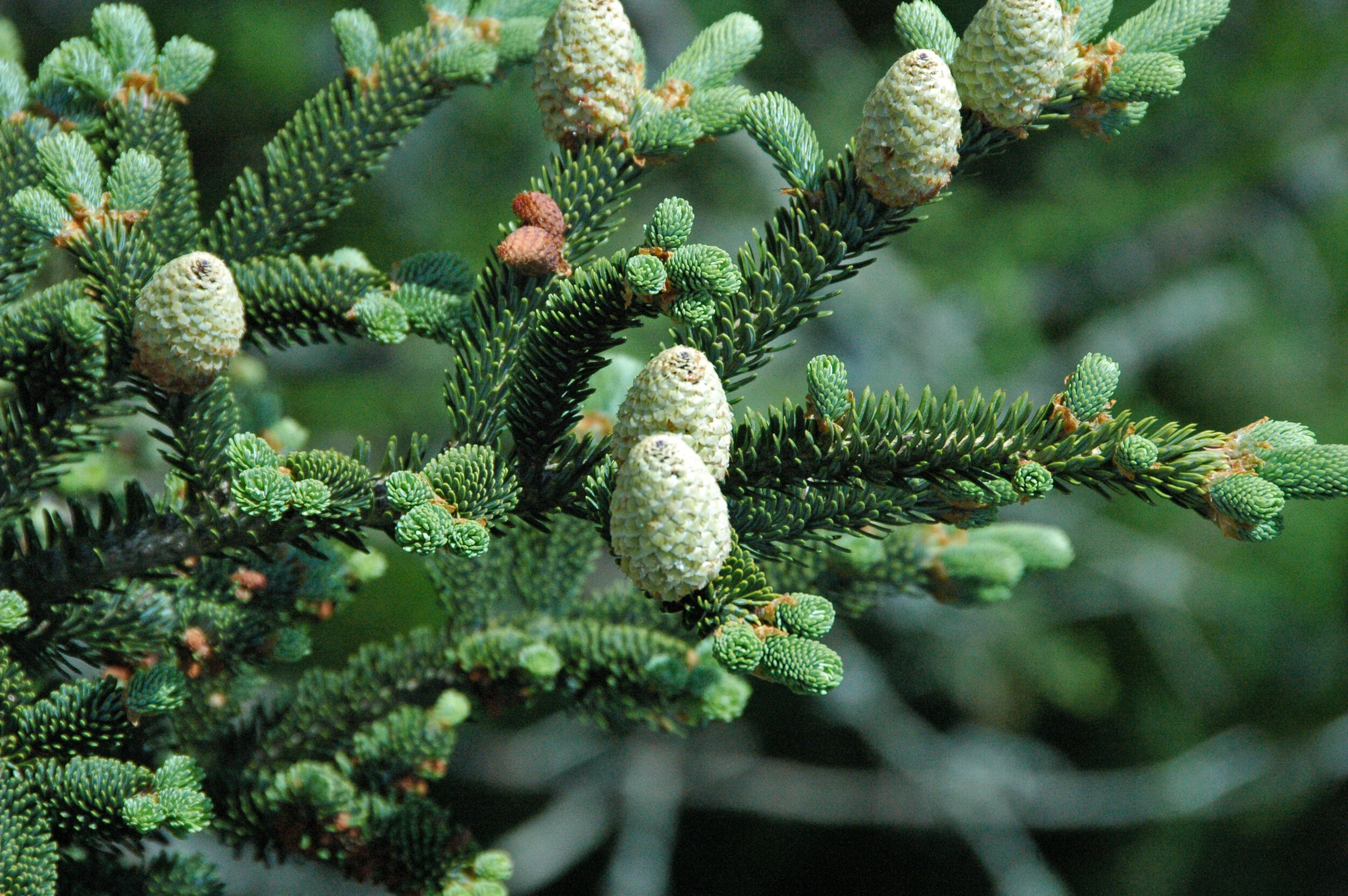
Growing up, Fraser fir (Abies fraseri) was a fairly common sight in our house. Each winter this species would usually win out over other options as the preferred tree for our living room during the holiday season. Indeed, its pleasing shape, lovely color, and soft needles have made it one of the most popular Christmas trees around the world. Amazingly, despite its popularity as a decoration, Fraser fir is so rare in the wild that it is considered an endangered species.
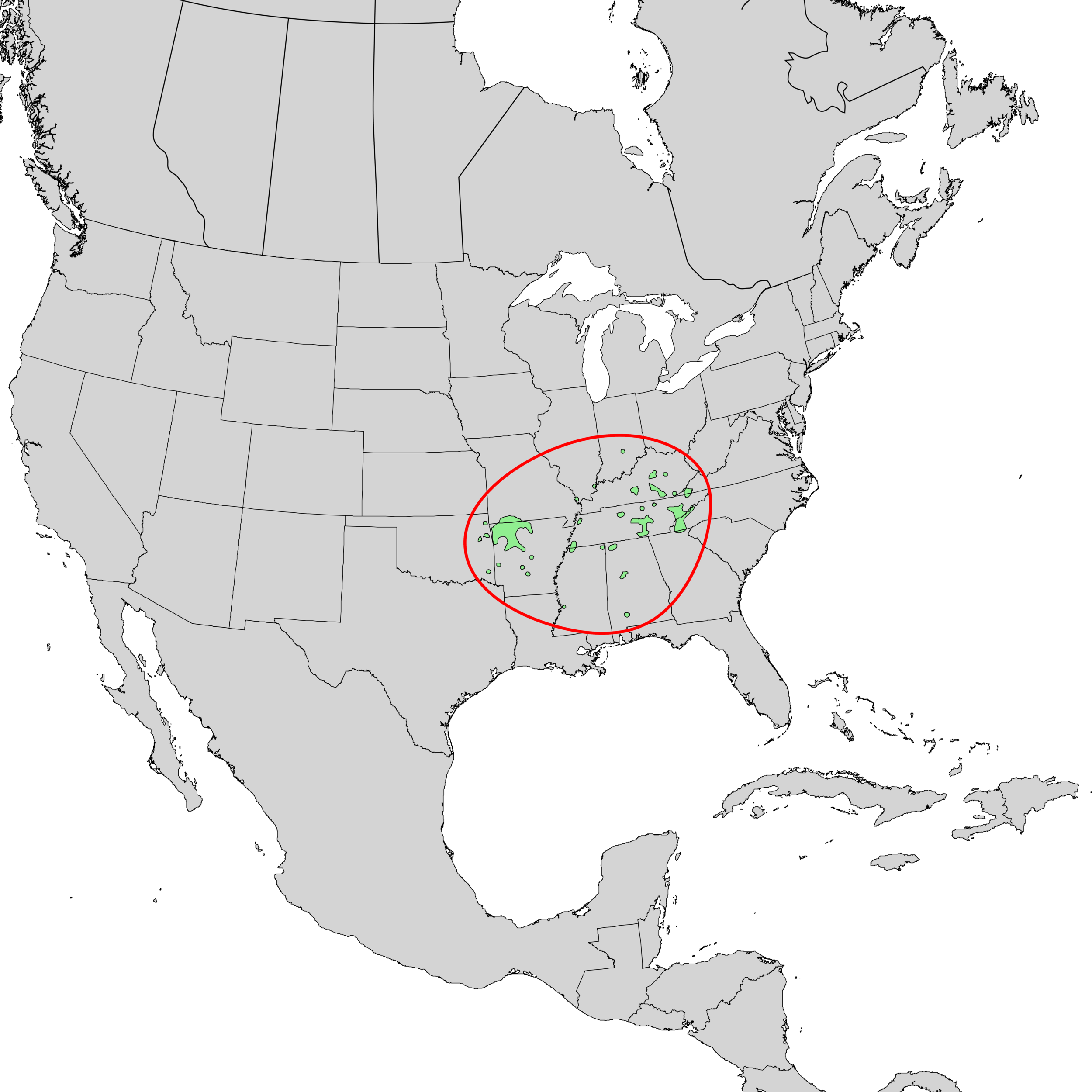
Fraser fir is native to only a handful of areas in the southern Appalachian Mountains. Together with red spruce (Picea rubens), this conifer makes up one of the rarest ecosystems on the continent - the southern Appalachian spruce-fir forest. Such forests only exist at elevations above 4,000 ft (1,200 m) from southwestern Virginia to western North Carolina and eastern Tennessee. The reason for this limited distribution is rooted in both modern day climate and North America’s glacial past.
USGS/Public Domain
Whereas anyone hiking through Appalachian spruce-fir forests could readily draw similarities to boreal forests found farther north, the Appalachian spruce-fir forests are nonetheless unique, hosting many species found nowhere else in the world. Indeed, these forests are holdovers from the Pleistocene when the southeast was much cooler than it is today. As glaciers retreated and the climate warmed, Appalachian spruce-fir forests “retreated” up the mountains, following their preferred climate zones until they hit the peaks of mountains and couldn’t go any further.
Indeed, Fraser fir is in large part limited in its distribution by temperature. This conifer does not perform well at high temperatures and is readily out-competed by other species under warmer conditions. Another factor that has maintained Appalachian spruce-fir forests at elevation is fog. The southern Appalachian Mountains host eastern North America’s only temperate rainforest and fog commonly blankets high elevation areas throughout the year. Research has shown that in addition to keeping these areas cool, fog also serves as an important source of water for Fraser fir and its neighbors. As fog condenses on its needles, these trees are able to absorb that water, keeping them hydrated even when rain is absent.
A view of an Appalachian spruce-fir forest from the Blue Ridge Parkway.
Due to its restricted habitat, Fraser fir has never been extremely common. However, things got even worse as Europeans colonized North America. Over the past two centuries, unsustainable logging and grazing practices have decimated southern Appalachian spruce-fir forests, fragmenting them into even smaller patches with no connectivity in between. In areas where thin, rocky soils were not completely washed away, Fraser fir seedlings did return, however, this was not always the case. In areas where soils were were lost, southern Appalachian spruce–fir forests were incapable of regenerating.
If the story ended there, Fraser fir and its habitat would still be in trouble but sadly, things only got worse with the introduction of the invasive balsam woolly adelgid (Adelges piceae) from Europe around 1900. Like the hemlock woolly adlegid, this invasive, sap-feeding insect has decimated Fraser fir populations throughout southern Appalachia. Having shared no evolutionary history with the adelgid, Fraser fir is essentially defenseless and estimates suggest that upwards of 90% of infect trees have been killed by the invasion. Although plenty of Fraser fir seedlings have sprung up in the wake of this destruction, experts fear that as soon as those trees grow large enough to start forming fissures in their bark, the balsam woolly adelgid will once again experience a massive population boom and repeat the process of destruction again.
Dead Fraser fir as seen from Clingman’s Dome. Photo by Brian Stansberry licensed under CC BY 3.0
The loss of Fraser fir from this imperiled ecosystem has had a ripple effect. Fraser fir is much sturdier than its red spruce neighbors and thus provides an important windbreak, protecting other trees from the powerful gusts that sweep over the mountain tops on a regular basis. With a decline in the Fraser fir canopy, red spruce and other trees are more susceptible to blowdowns. Also, the dense, evergreen canopy of these Appalachian spruce-fir forests produces a unique microclimate that fosters the growth of myriad mosses, liverworts, ferns, and herbs that in turn support species like the endangered endemic spruce-fir moss spider (Microhexura montivaga). As Fraser fir is lost from these areas, the species that it once supported decline as well, placing the whole ecosystem at risk of collapse.
Luckily, the plight of this tree and the habitat it supports has not gone unnoticed by conservationists. Numerous groups and agencies are working on conserving and restoring Fraser fir and southern Appalachian spruce-fir forests to at least a portion of their former glory. This is not an easy task by any means. Aside from lack of funding and human power, southern Appalachian spruce-fir forest conservation and restoration is hindered by the ever present threat of a changing climate. Fears that the life-giving fog that supports this ecosystem may be changing make it difficult to prioritize areas suitable for reforestation. Also, the continued threat from invasive species like the balsam woolly adelgid can hamper even the best restoration and conservation efforts. Still, this doesn’t mean we must give up hope. With continued collaboration and effort, we can still ensure that this unique ecosystem has a chance to persist.
Please visit the Central Appalachian Spruce Restoration Initiative (CASRI) website to learn more!
Photo Credits: [1] [2] [4] [5]
Further Reading: [1] [2] [3] [4]







![[SOURCE]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/544591e6e4b0135285aeb5b6/1446693514555-CSXK7BS2HWC1063O8MG7/image-asset.jpeg)